PCI Security Standards: 12 Core Requirements for All 4 Levels
The rising tide of digital threats shows no signs of receding. Is your business prepared to withstand a cybercrime wave?
Published April 5, 2025.

In 2023, cybercrime cost the United States $12.5 billion. And phishing attacks and data breaches led this surge. For businesses handling sensitive cardholder data, robust security is no longer optional—it's essential.
» Read: The Cloud Might Not Be Safe Anymore—And We Should All Be Concerned
Enter the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). This framework ensures companies processing credit card information follow strict security practices. PCI DSS compliance protects data and shields businesses from the severe fallout of breaches.
This article explores the core aspects of PCI DSS, its benefits, compliance levels, and the specific requirements organizations must meet.
» Achieve PCI compliance with ease: Get expert guidance every step of the way
What Is PCI DSS?
PCI DSS is a set of security requirements to protect cardholder data established by 6 major credit card companies:
- VISA
- Discover
- JCB
- Mastercard (MC)
- American Express (AMEX)
- UnionPay
It applies to any organization involved in processing, storing, or transmitting credit card information. Unlike other security standards (such as ISO 27001) which focus on general data protection, PCI DSS specifically addresses the security of credit card information.
The standard offers clear, actionable guidelines that reduce data breach risks and are essential for any business involved in payment card transactions.
» Enhance your understanding of PCI DSS compliance
4 Benefits of PCI DSS Compliance
Adhering to PCI DSS standards offers several advantages for businesses:
- Enhanced security posture: Implementing PCI DSS strengthens your organization's overall security framework. It covers various aspects, from network defenses to access controls, and can significantly reduce your vulnerability to cyberattacks.
- Increased customer trust: PCI DSS compliance reassures customers that their credit card information is handled securely. This trust can lead to increased customer retention and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
- Avoidance of fines and penalties: Non-compliance with PCI DSS can result in hefty fines. Compliance helps you avoid these financial repercussions and the associated indirect costs of data breaches, including legal fees and customer compensation.
- Competitive advantage: PCI DSS compliance can be a significant selling point, distinguishing your organization from non-compliant competitors. This is particularly advantageous in industries where security is a primary concern for customers.
» Learn more about the benefits of PCI DSS compliance
Levels of PCI Compliance
PCI compliance levels categorize businesses based on their annual transaction volume. These levels help tailor the compliance requirements to the company's size and complexity. Merchants and service providers have distinct levels of compliance, each with specific criteria and validation procedures.
For Merchants
Merchants are entities that accept payments from any of the six members of the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC):
- VISA
- Discover
- JCB
- Mastercard (MC)
- American Express (AMEX)
- UnionPay
The following table outlines the PCI compliance requirements for different merchant levels:
| Level | Annual Transaction Volume | Compliance Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Over 6 million transactions per year | • Annual Report on Compliance (ROC) by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA)/internal audit if signed by an officer of the company • Quarterly network scans by Approved Scanning Vendor (ASV) |
| 2 | 1 to 6 million transactions per year | • Annual Self-Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) to evaluate compliance • Attestation of Compliance (AOC) for each SAQ • Quarterly ASV network scans |
| 3 | 20k to 1 million eCommerce transactions per year | • Annual SAQ and AOC • Quarterly ASV network scans |
| 4 | Under 20k eCommerce transactions per year/ Under 1 million annual transactions of any type | • Annual SAQ and AOC • Recommended quarterly ASV network scans |
For Service Providers
Service providers are business entities that process, store, or transmit cardholder data on behalf of another entity. This also includes companies that provide services that control or could impact the security of cardholder data.
Note: A merchant that accepts payment cards could also be a service provider—if the services result in storing, processing, or transmitting cardholder data on behalf of other merchants or service providers.
The table below shows the PCI DSS compliance requirements for service providers:
| Level | Annual Transaction Volume | Compliance Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Over 300k transactions per year | • Annual ROC by a QSA • Quarterly ASV network scans |
| 2 | Up to 300k transactions per year | • Annual SAQ • Quarterly network scans by an ASV |
Note: These requirements are subject to change by the brands themselves. Additionally, an acquirer can impose or decide on a different level for their merchants based on several factors.
For guidance on selecting the appropriate SAQ, consult official PCI SSC resources. Alternatively, contact GRSee's cyber security experts for advice.
GRSee specialists understand that achieving and maintaining PCI DSS compliance is no easy feat. So, to help streamline your compliance efforts, the team offers expert consulting and tailored implementation support. The goal is to help you meet the necessary standards while enhancing your overall security posture.
» Discover how to succeed with PCI DSS compliance
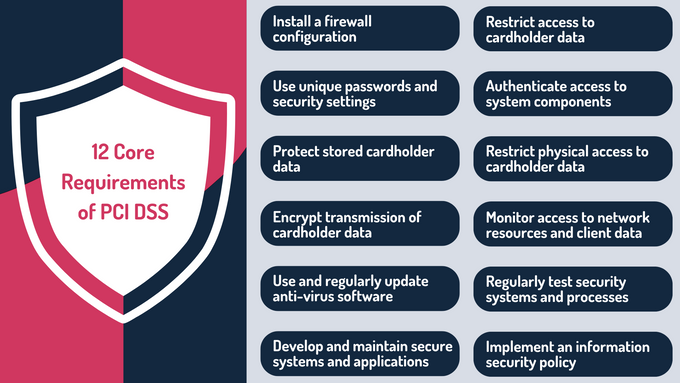
12 Core Requirements of PCI DSS
PCI DSS comprises 12 essential requirements. These standards form the foundation of cardholder data security:
- Deploy and maintain firewalls to shield networks from unauthorized access. Control incoming and outgoing network traffic with security rules.
- Replace default system passwords and security parameters. This step prevents easy exploitation by attackers.
- Encrypt stored cardholder data to ensure that unauthorized parties cannot read the information, even if they access it.
- Use encryption protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) when sending cardholder data over public networks.
- Install and update anti-virus and anti-malware solutions on all systems. This helps detect and block the latest threats.
- Adopt secure development practices. Update software regularly and patch vulnerabilities promptly. Also, follow a Secure Software Development Life Cycle (SSDLC) to address security issues during development.
- Implement role-based access controls (RBAC). This ensures that only authorized personnel can view sensitive information, which reduces the risk of data exposure.
- Use strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA). This verifies that only legitimate users can access system components and data.
- Implement access controls and surveillance measures to protect sensitive information from physical threats. Monitor and log physical access regularly.
- Deploy robust logging mechanisms to track user activities and identify suspicious behavior.
- Conduct frequent security assessments, including vulnerability scans and penetration tests. This helps identify weaknesses and validate security control effectiveness.
- Create and maintain comprehensive security policies. These should provide guidelines for protecting sensitive information and outline employee responsibilities. Conduct regular training to reinforce these policies.
» Stay PCI compliant and ensure your business meets all security standards
Consequences of PCI Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with PCI DSS can result in severe repercussions. Credit card companies may impose substantial fines, ranging from thousands to millions of dollars. (The exact amount depends on the severity of non-compliance and any resulting data breaches.) Organizations might also face higher transaction fees and increased scrutiny from acquiring banks, which can strain financial stability.
Additionally, non-compliance can inflict lasting damage to a company's reputation. Data breaches erode customer trust and generate negative publicity. This loss of confidence often leads to decreased sales and long-term harm to the brand. You may need to undergo costly breach investigations and remediation efforts to address vulnerabilities, too.
» Avoid these common PCI DSS pitfalls
Keep Your Customers Safe in Today's Digital Age
PCI DSS compliance is more than just a regulatory requirement—it's a crucial step in protecting your business and customers in our connected world. By implementing these standards, you safeguard sensitive data and demonstrate your commitment to security.
Remember, cybersecurity is an ongoing process. Stay informed about the latest threats and updates to PCI DSS. Also, regularly assess your systems and processes to ensure continued compliance. With the right approach and support, you can turn PCI DSS compliance into a competitive advantage, building trust and resilience in an increasingly digital world.
» Go beyond basic compliance: Find out how penetration testing can enhance your security posture