What Is CMMC Certification? A Comprehensive Guide
Learn what CMMC certification is, why it matters for defense contractors, and how to achieve compliance under the latest CMMC standards.
Published March 30, 2025.

In today's increasingly complex cybersecurity landscape, defense contractors must meet stringent security requirements to maintain eligibility for government contracts. One such requirement is achieving CMMC certified status, a critical step in ensuring that contractors protect sensitive information within the Department of Defense (DoD) supply chain. Understanding CMMC standards is essential for any organization aiming to enhance their cybersecurity practices while remaining compliant.
In this blog, we will break down the CMMC compliance definition and explore how organizations can navigate the process of meeting these vital standards to safeguard their operations and reputation.
» Contact us to navigate CMMC and ensure long-term compliance success
What Is the CMMC?
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) is a framework established by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) to ensure that defense contractors within the Defense Industrial Base (DIB) implement robust cybersecurity practices to safeguard Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
» Understand why you need compliance
Key Security Threats That CMMC Aims to Mitigate
The CMMC certification framework is designed to help defense contractors address critical cybersecurity threats more efficiently. By establishing clear security requirements, it reduces vulnerabilities that could compromise sensitive information.
Key security threats include:
- Phishing attacks: In 2015, a phishing attack on the Joint Chiefs of Staffs' unclassified email servers left 4,000 personnel without access for 11 days, demonstrating the disruptive impact of such attacks.
- Insider threats: These threats are difficult to detect and eliminate. CMMC focuses on measures to minimize the risks posed by individuals within an organization.
- Supply chain vulnerabilities: The collapse of IronNet, the cybersecurity firm founded by former NSA head Keith Alexander, due to fraud charges and financial troubles highlights the need to strengthen security across the defense supply chain.
» Understand the disasters you can avoid by tackling cybersecurity on time
CMMC vs. NIST 800-171 vs. ISO 27001 vs. SOC 2
| Framework | Scope and Applicability | Compliance Obligations | Real World Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMMC | Mandatory for DoD contractors, focusing on protecting CUI and FCI within the DoD supply chain | Levels 2 and 3 require third-party certification (C3PAOs) for thorough compliance verification | Non-compliance can result in losing DoD contracts, directly affecting viability in the military sector |
| NIST 800-171 | Mostly a self-evaluation tool for contractors handling CUI in federal agencies outside the DoD | Relies on self-assessments unless specified in contracts; rarely requires third-party audits | Compliance supports government contract eligibility but lacks CMMC’s strict third-party audit enforcement |
| ISO 27001 | A global standard for ISMS, applicable to all industries with flexible implementation | Optional but often pursued for competitive advantage; requires independent audits by accredited organizations | Often pursued for client trust and market distinction rather than legal requirements |
| SOC 2 | Focuses on how service providers handle client information, widely used in commercial sectors | Requires independent audits but is optional unless required by clients or contracts | More about reputation and client expectations than contract eligibility |
» Learn more about the merits of adopting ISO 27001/SOC2
Cybersecurity Controls, Protection, and Impact at Each Level
CMMC 2.0 introduced significant changes to simplify and enhance the certification process compared to CMMC 1.0. The framework was reduced from five levels to a more manageable three: Foundational (Level 1), Advanced (Level 2), and Expert (Level 3). This simplification keeps the emphasis on important security procedures while reducing complexity.
Level 1: Foundational
- Security requirements: Focuses on 17 basic controls from FAR Clause 52.204-21 to protect FCI. Key practices include password management, patching, and access control.
- Scaling for protection: Provides foundational safeguards against common threats like phishing and unauthorized access.
- Assessment requirements: Organizations conduct annual self-assessments, attested by a senior executive. These assessments verify compliance with 17 basic FAR Clause 52.204-21 controls.
- Impact on businesses: Self-assessments reduce costs and administrative burdens, making compliance accessible for small businesses.
- Compliance expenses: Low, as the third-party auditing is not mandatory. Ideal for contractors who must handle FCI but non-sensitive Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
Level 2: Advanced
- Security requirements: Implements 110 controls from NIST SP 800-171 to protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
- Scaling for protection: Addresses intermediate threats like supply chain attacks and insider risks.
- Assessment requirements: High-priority contracts undergo third-party audits by Certified Third-Party Assessor Organizations (C3PAOs) every three years. For non-critical contracts, organizations can perform annual self-assessments to verify compliance.
- Impact on businesses: Third-party assessments increase costs and require detailed preparation. However, they provide higher assurance of compliance, improving eligibility for sensitive DoD contracts.
- Compliance expenses: Medium, due to third-party audits and the implementation of advanced controls. Ideal for contractors who handle sensitive CUI.
Level 3: Expert
- Security requirements: Builds on Levels 1 and 2 with additional controls from NIST SP 800-172. Focuses on advanced protections like system hardening.
- Scaling for protection: Mitigates sophisticated attacks targeting national security data.
- Assessment requirements: Must be put to the test by the government in order to determine adherence to the highest security requirements.
- Impact on businesses: These are the most demanding and costly evaluations, requiring substantial preparation and the execution of advanced security measures.
- Compliance expenses: High, due to the advanced controls being complicated and requiring government scrutiny. This certification is typically restricted to contractors handling highly sensitive national security information.
» Do you have a startup plan? Check out these cyber tips
Take Note: The core requirements for CMMC compliance depend on the maturity level an organization needs to achieve. Each level has specific cybersecurity controls and practices that must be implemented. The levels are cumulative, meaning an organization must also demonstrate achievement of the preceding lower levels.
3 Factors Influencing the Cost of CMMC Certification
- Security upgrades: You may need to invest in hardware, software, and infrastructure upgrades to meet compliance. These costs include one-time expenses, such as system enhancements, and ongoing maintenance to ensure continued security.
- Internal compliance efforts: Achieving certification requires staff training, policy development, and extensive documentation. Many organizations also hire consultants to streamline preparation and ensure a smoother certification process.
- Scope of CUI: The volume and distribution of CUI directly affect costs. If your organization handles large amounts of CUI across multiple systems, you will likely face higher expenses for securing data flows and implementing necessary controls.
Practical Tips for Minimizing CMMC Compliance Costs
Maximize existing compliance investments
- Many CMMC requirements align with existing security frameworks, allowing contractors already following these standards to build on their current controls rather than starting from scratch.
- Impact: This approach reduces costs associated with security improvements and simplifies the assessment process, particularly for Level 2 compliance.
Use a CMMC enclave approach
- Instead of upgrading the entire IT infrastructure, organizations can isolate systems containing CUI within a secure enclave that meets CMMC standards, reducing the overall compliance scope.
- Impact: Enclaves lower both implementation and assessment costs while ensuring compliance for critical systems, making this method especially beneficial for small- to mid-sized contractors.
Outsource compliance support
- Partnering with Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) or CMMC consultants helps streamline the implementation process, manage documentation, and facilitate assessments.
- Impact: Outsourcing removes the need for in-house expertise, saving time and reducing costs while ensuring compliance with third-party or government-led assessments.
» Read more: What is good compliance?
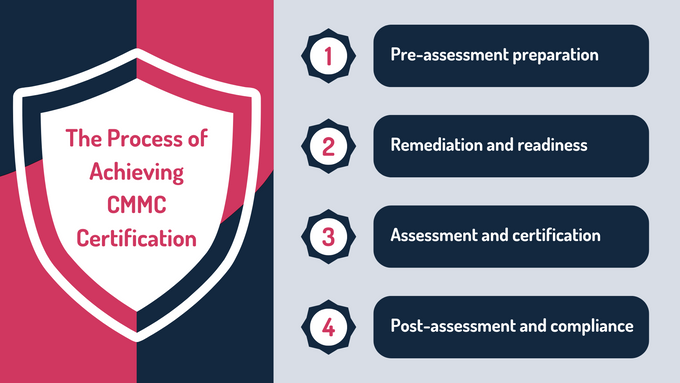
The Process of Achieving CMMC Certification
1. Pre-Assessment Preparation
- Identify CMMC level: Determine the required maturity level (1, 2, or 3) based on contract needs and data sensitivity (FCI or CUI).
- Conduct a gap analysis: Compare current security practices against CMMC requirements to identify deficiencies.
- Develop a system security plan (SSP): Document IT systems, security measures, and data flows.
Tip: Work with a Registered Provider Organization (RPO) for expert guidance.
2. Remediation and Readiness
- Address gaps: Implement necessary security controls, aligning with NIST SP 800-171/172 for Levels 2 and 3.
- Establish POA&Ms: Create a plan to resolve risks and deficiencies.
- Conduct internal assessments: Verify readiness before the formal evaluation.
3. Assessment and Certification
The assessment process consists of four key phases:
- Scope review
- Evidence collection
- Staff interviews
- Discussion of findings
Each phase ensures that the organization meets the necessary security controls and practices for the targeted maturity level. Organizations must also schedule an assessment with a C3PAO to evaluate their compliance with CMMC requirements.
4. Post-Assessment and Compliance
- Address deficiencies: If any deficiencies are identified during the assessment, organizations have 90 days to implement corrective actions and bring their security practices into compliance.
- Certification decision: Once the assessment is complete, the CMMC Accreditation Body (CMMC-AB) reviews the findings and determines whether the organization meets the required maturity level. If approved, the certification is granted and remains valid for three years.
- Maintain compliance: To retain certification, organizations must continuously monitor their security systems, update their SSPs, and ensure they remain compliant in preparation for future assessments and re-certification.
» Enhance your organization's security with the CIA triad
How GRSee Consulting Can Help with CMMC Compliance
Navigating CMMC certification can be complex, but with the right support, you can streamline the process and meet compliance requirements efficiently. GRSee Consulting simplifies your journey with tailored services designed to support you at every stage. Our goal is to help you achieve compliance while strengthening your overall cybersecurity posture.
Our services include:
- CMMC readiness assessments: We evaluate your current cybersecurity posture and identify any gaps that need to be addressed.
- Remediation planning and implementation: Our team helps you address security deficiencies to ensure alignment with CMMC standards.
- Policy and procedure development: We create comprehensive documentation that meets all compliance requirements.
- Assessment and audit preparation: We guide you through the process of preparing for third-party evaluations or government audits, ensuring you are ready.
» Contact us to guide you through your CMMC certification with confidence