Key Changes in PCI DSS 4.0 Requirements: A Breakdown for Businesses
Explore the key changes in PCI DSS 4.0, highlighting how businesses can align their security measures with the latest compliance requirements. From expanded MFA mandates to continuous compliance, this article provides readers with actionable strategies to safeguard payment data and maintain customer trust.
Published April 5, 2025.

In 2023, the US faced a record-breaking 3,205 data breaches, compromising the personal information of approximately 353 million individuals. As cyber threats evolve, businesses must adapt to ensure their security measures not only address current vulnerabilities but also anticipate future challenges. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) has long served as the benchmark for safeguarding cardholder data, and the release of PCI DSS 4.0 marks a significant step forward in strengthening payment security.
PCI DSS 4.0 introduces comprehensive updates designed to address emerging risks, enhance flexibility, and promote continuous compliance. This evolution goes beyond periodic audits, encouraging organizations to embed security into their daily operations. As businesses navigate these changes, understanding and implementing the new requirements will be vital for protecting sensitive data and maintaining customer trust in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
» Meet PCI DSS requirements easily: Contact us
What’s New in PCI DSS 4.0?
PCI DSS 4.0 marks a major step forward in securing payment data, bringing updated requirements to tackle today’s evolving cyber threats. With expanded authentication and a focus on continuous compliance, it promotes a proactive, trust-building approach to data protection.
Here’s a closer look at the key changes:
» Not sure about PCI DSS? Here are the benefits of PCI DSS compliance
1. Expanded MFA Requirements
Under PCI DSS 4.0, the scope of multi-factor authentication (MFA) has been broadened significantly, ensuring stricter access control across all systems within the cardholder data environment (CDE). This change strengthens one of the most fundamental components of secure access management.
Key Changes
- MFA is now required for all users accessing the CDE, not just administrators or remote users.
- Specific emphasis on implementing phishing-resistant MFA, such as hardware tokens and biometrics (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition).
- Applies to both onsite and remote access points.
Impact
- Strengthens access security across hybrid and cloud infrastructures, which are often targeted by attackers.
- Reduces the risk of credential theft, a common vector for cyberattacks, particularly in phishing schemes.
- Enhances traceability and accountability by linking every access attempt to an individual user, aiding audits and investigations.
» Don't fall for these PCI DSS myths
2. Customized Approach
PCI DSS 4.0 introduces a customized approach to provide flexibility for organizations with advanced security systems. This option allows businesses to implement alternative controls while meeting compliance objectives, catering to the unique needs of organizations that already have sophisticated security measures in place.
Key Features
Organizations can propose custom security measures as alternatives to specific PCI DSS requirements:
- Comprehensive documentation of the custom controls, outlining their purpose and function.
- A clear explanation of how the custom approach aligns with the security objectives of PCI DSS standards.
- Validation by a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) to ensure compliance is not compromised.
Industries Most Likely to Benefit
- Technology and cloud providers: Flexibility to tailor encryption, data isolation, and traffic monitoring practices to align with advanced technologies.
- Financial institutions: Customized tokenization and secure transaction monitoring systems to align with internal policies and regulatory frameworks.
- Enterprises with mature security programs: Ensures existing sophisticated controls can be leveraged without redundant modifications.
» Understand the differences between symmetric and asymmetric encryption
3. Continuous Compliance
One of the most transformative updates in PCI DSS 4.0 is the shift from periodic audits to a focus on continuous compliance. This model encourages organizations to adopt ongoing monitoring and proactive risk assessment and management practices, embedding compliance into daily operations.
» Make sure you understand what's involved in the risk assessment process
Key Requirements
Organizations must implement automated tools for:
- Real-time log monitoring to detect and flag anomalies immediately.
- Vulnerability detection and patch management to address weaknesses proactively.
- Anomaly detection and incident response mechanisms that support quick action when breaches are attempted.
- Move away from solely relying on annual assessments by incorporating continuous compliance checks.
Operational Impact
- Reduces compliance drift by ensuring that controls remain effective and operational throughout the year rather than becoming outdated between audits.
- Promotes cross-functional collaboration between IT, operations, and security teams to address compliance and security gaps in real-time.
- Shifts compliance from being a point-in-time event to an integral part of organizational workflows, fostering a culture of ongoing security improvement.
4. Enhanced Third-Party Risk Management
With increasing reliance on third-party vendors and service providers, PCI DSS 4.0 introduces stricter measures for managing risks associated with external partners. This ensures that vendor vulnerabilities do not compromise the security of the cardholder data environment (CDE).
Contracts with vendors must:
- Clearly define security responsibilities, including adherence to specific PCI DSS controls.
- Mandate regular security assessments to ensure vendors remain compliant over time.
- Establish formal processes to validate vendor compliance, including audit reviews and risk assessments.
» Here's what you should know before hiring a risk assessment provider
Implications for Cloud and Outsourced Services
Organizations using cloud services or outsourced IT operations must:
- Perform rigorous due diligence before onboarding a vendor.
- Regularly validate that the vendor’s security measures align with PCI DSS standards.
- Implement ongoing monitoring processes to ensure third-party activities within the CDE remain compliant.
This increased emphasis on vendor risk management highlights the importance of securing the entire supply chain, ensuring that external partnerships do not become a weak link in the organization’s security framework.
» Did you know? The cloud might not be safe anymore
5. Emerging Threats
As cyber threats become more sophisticated, PCI DSS 4.0 introduces updated guidelines to address evolving risks. The standard prioritizes defenses against advanced persistent threats (APTs) and phishing attacks, which target organizations through multiple vectors and exploit both technical and human vulnerabilities.
PCI DSS 4.0 emphasizes:
Comprehensive Defense Strategies
- Reinforce endpoint security measures to detect and prevent unauthorized access.
- Implement continuous monitoring tools to identify unusual patterns or behavior that could indicate an ongoing attack.
- Strengthen incident response plans to ensure swift action against detected threats.
- Conduct regular vulnerability assessments to identify and patch weak points.
- Enhanced encryption and tokenization requirements to safeguard sensitive data from being intercepted or exfiltrated.
These measures ensure that organizations can detect, mitigate, and respond to APTs effectively, protecting their cardholder data environment from sophisticated attackers.
Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing and social engineering attacks have evolved beyond email, now targeting organizations through various communication channels, including SMS (smishing), voice calls (vishing), and social media. PCI DSS 4.0 provides updated guidelines to address these pervasive threats:
- Expanded multi-factor authentication (MFA) requirements, reducing the risk of credential theft even if employees fall victim to phishing.
- Emphasis on implementing phishing-resistant authentication methods, such as hardware tokens or biometric verification.
| Key Change | Overview | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Expanded MFA Requirements | Requires multi-factor authentication for all users accessing the cardholder data environment (CDE). | Strengthens access control, reduces credential theft risk, and ensures secure authentication. |
| Customized Approach | Allows organizations to implement alternative controls tailored to their operations. | Provides flexibility, supports innovation, and requires validation to maintain compliance objectives. |
| Continuous Compliance | Shifts from periodic audits to real-time monitoring and proactive risk management. | Promotes year-round compliance, reduces compliance drift, and integrates security into daily workflows. |
| Enhanced Third-Party Risk Management | Introduces stricter measures for managing third-party vendor compliance and oversight. | Minimizes vendor vulnerabilities, ensures secure supply chains, and enforces accountability through contracts. |
| Emerging Threats | Focuses on addressing advanced persistent threats (APTs) and phishing/social engineering attacks. | Strengthens technical defenses, emphasizes employee training, and reduces susceptibility to evolving threats. |
Industry-Specific Impacts
The updates in PCI DSS 4.0 affect industries in unique ways, driven by their operational complexities and specific security challenges. Understanding how these changes apply across sectors such as retail, e-commerce, and small businesses can help organizations align their compliance efforts with industry realities and address potential roadblocks effectively.
1. Retail
Retailers, especially those operating large-scale environments with physical point-of-sale (POS) systems, face distinct challenges in implementing PCI DSS 4.0 requirements due to the diversity of systems and the dynamic nature of their workforce.
Key challenges include:
- MFA challenges for POS systems: Deploying multi-factor authentication (MFA) for POS systems often involves integrating modern authentication methods into older legacy systems. This can require significant upgrades to hardware and software, creating both technical and financial challenges for retailers operating on tight margins.
- Employee training with high turnover: The retail industry experiences frequent staff turnover, requiring ongoing training programs to ensure new employees are aware of and adhere to PCI DSS 4.0 security protocols. Maintaining consistent compliance with a changing workforce adds operational complexity.
Despite these challenges, retailers must prioritize security to protect customer payment data and maintain trust. Successful implementation of PCI DSS 4.0 can strengthen customer loyalty and protect against costly data breaches.
2. E-Commerce
E-commerce businesses operate in fully digital environments, making them especially susceptible to cyber threats targeting online payment systems and customer data. PCI DSS 4.0 introduces measures that directly address the needs of this sector.
Key challenges include:
- Meeting encryption standards: E-commerce platforms must ensure payment gateways comply with updated encryption and tokenization standards to secure sensitive cardholder data. This often involves upgrading backend systems and integrating advanced encryption technologies, which can require collaboration with third-party payment processors.
- Global authentication challenges: Serving a global customer base comes with the challenge of implementing secure authentication methods that meet varying regional regulations and customer expectations. Balancing security with user convenience is key, especially in regions with less robust infrastructure or differing legal requirements.
Adopting PCI DSS 4.0 positions e-commerce businesses as trustworthy and secure, reducing cart abandonment due to security concerns while fortifying defenses against cyberattacks.
3. Small Businesses
Given their limited resources and typically smaller scope of operations, small businesses face unique challenges and opportunities under PCI DSS 4.0. While compliance can appear daunting, it also provides a path for small businesses to strengthen their reputation and security posture.
Key challenges include:
- Cost implications: For small businesses, the cost of implementing PCI DSS controls can be significant. However, these businesses often have smaller Cardholder Data Environments (CDEs), simplifying the compliance process and reducing overall resource requirements.
- Leveraging compliance tools: Small businesses can take advantage of compliance automation platforms to streamline the process. These tools simplify evidence collection, automate monitoring, and reduce the manual effort needed to stay compliant. With this technology, small businesses can achieve PCI DSS compliance without overwhelming their limited IT teams.
For small businesses, PCI DSS 4.0 provides an opportunity to adopt industry best practices early, building a strong security foundation that can scale as the organization grows.
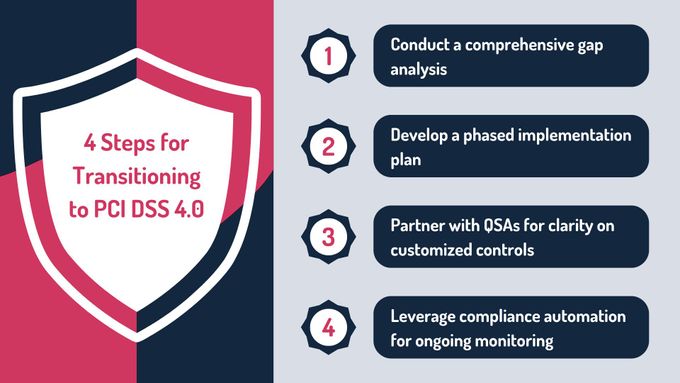
How to Transition to PCI DSS 4.0
Transitioning to PCI DSS 4.0 requires a structured approach to ensure compliance while minimizing disruption to your organization’s operations. With these practical steps, businesses can effectively align their security measures with the new requirements and maintain a robust defense against evolving threats.
1. Conduct a Comprehensive Gap Analysis
Begin the transition by conducting a detailed assessment of your current compliance posture against the updated PCI DSS 4.0 requirements. This involves mapping existing controls to the new standards, identifying gaps, and evaluating technical, procedural, and operational areas that need updates.
Prioritizing high-risk gaps allows organizations to address vulnerabilities in their CDE before they become critical. A well-executed gap analysis provides the foundation for an effective transition strategy.
2. Develop a Phased Implementation Plan
Given the complexity of the PCI DSS 4.0 requirements, a phased implementation plan ensures that progress is made without overwhelming resources. This involves breaking down the transition into manageable steps, starting with high-priority areas such as MFA deployment and encryption upgrades.
To ensure steady progress, organizations should establish clear timelines and milestones while strategically allocating resources—including personnel, budgets, and technical tools. This phased approach allows for steady improvements without disrupting operational efficiency.
3. Partner With QSAs for Clarity on Customized Controls
Customized controls introduced in PCI DSS 4.0 offer flexibility but require expert validation to ensure compliance. Engaging a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) provides valuable clarity on how to implement and document these controls effectively.
Experienced QSAs can ensure that customized measures meet the intended security outcomes while documenting their rationale in alignment with PCI DSS objectives. Partnering with a QSA helps to reduce ambiguity and mitigate the risk of non-compliance.
» Learn more about cyberservices
4. Leverage Compliance Automation for Ongoing Monitoring
The shift toward continuous compliance in PCI DSS 4.0 highlights the importance of robust monitoring tools. Compliance automation simplifies this process by enabling real-time log collection, vulnerability scanning, and anomaly detection.
Organizations using automation tools can maintain audit readiness and seamlessly integrate compliance practices into their daily workflows. Reducing manual effort allows businesses to focus on strategic security improvements while maintaining year-round compliance.
» Need more help? Here's how to build a robust PCI DSS security strategy
Simplify PCI DSS 4.0 Compliance With GRSee
Achieving and maintaining PCI DSS 4.0 compliance can be a complex and resource-intensive process, but GRSee Consulting is here to make it easier. We offer end-to-end services that guide organizations through every step of the compliance journey, from initial advisory and gap analysis to successful audits and ongoing maintenance. Our team of experts ensures a seamless process, tailored to your specific needs.
At GRSee, we focus on scope-reduction strategies to streamline the compliance process. Our goal is to identify and minimize your CDE as well as help you reduce both risks and costs while maintaining the highest security standards. Additionally, we leverage advanced compliance technologies to accelerate implementation, enhance monitoring, and ensure your organization stays audit-ready year-round.
» Ready to achieve PCI DSS compliance? Contact us to learn about our startup and enterprise services