Beyond Compliance: Leveraging Penetration Testing and Training in PCI DSS 4.0.1
Discover how PCI DSS penetration testing safeguards cardholder data and ensures compliance with PCI DSS 4.0.1. Learn its importance, methodologies, and actionable steps to integrate it into your compliance strategy.
Published April 5, 2025.

In 2023, the average cost of a data breach reached an astonishing $4.45 million globally, underscoring the critical importance of robust security measures for businesses of all sizes. Cybercriminals constantly evolve their tactics, targeting vulnerabilities to exploit sensitive payment data. For organizations handling payment card information, achieving and maintaining PCI DSS compliance is not just a regulatory obligation—it’s a safeguard against financial loss, reputational damage, and eroding customer trust.
This article, authored by Software Secured, a trusted penetration testing provider and proud GRSee partner, dives into the essential role penetration testing plays in PCI DSS compliance. From understanding key requirements to exploring practical solutions, we’ll address common challenges and provide actionable insights to help your business stay one step ahead in securing its systems and protecting customer data.
» Let GRSee take your business security beyond compliance: Set a FREE session with our experts
What Is a Penetration Test?
A penetration test, often referred to as a pentest, is a specialized security test designed to uncover exploitable vulnerabilities in your computer systems, networks, or applications.
Conducted by third-party experts, penetration testing for compliance offers a comprehensive assessment of your security posture. This includes identifying vulnerabilities, providing detailed replication steps, and offering actionable remediation strategies. The ultimate goal is to help organizations reduce risks while fulfilling compliance requirements, such as those outlined in a PCI DSS strategy.
For organizations seeking continuous protection, Penetration Testing as a Service (PTaaS) combines cybersecurity penetration testing for PCI compliance. PTaaS also combines traditional penetration tests with ongoing security consulting and fix verification. While a one-time pentest is valuable for establishing a security baseline, pentesting for compliance ensures repeated assessments and proactive guidance to address evolving threats.
Types of Penetration Testing
| Type of Testing | Explanation | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Black-Box Testing | Testers simulate an external attack with no prior knowledge of the system. | Identifying vulnerabilities exploitable by external attackers. |
| White-Box Testing | Testers have full access to the system’s architecture, source code, and internal documentation. | Provides a detailed evaluation of internal security controls and configurations. |
| Gray-Box Testing | Combines elements of black-box and white-box testing, with testers having limited knowledge of the system. | Mimics insider threats or compromised users to identify vulnerabilities within the system. |
» Learn more: Types of penetration testing
Penetration Testing Tools
A wide range of tools is available to assist penetration testers in uncovering vulnerabilities and assessing security measures. Here are some popular options and their use cases:
- Nmap: Network discovery and vulnerability scanning.
- Burp Suite: Testing web application security, including identifying SQL injections and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Metasploit: Exploiting vulnerabilities to demonstrate potential impacts.
- OWASP ZAP: Identifying and analyzing web application vulnerabilities.
- Wireshark: Network traffic analysis and troubleshooting.
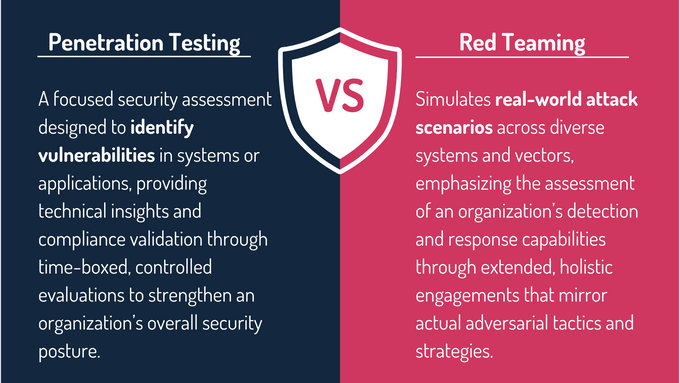
Red Teaming vs. Penetration Testing
While both penetration testing and red teaming aim to improve organizational security, they differ significantly in scope and methodology:
Penetration Testing
- Aimed at identifying vulnerabilities in specific systems or applications.
- Focused on technical assessments and compliance requirements.
- Typically time-boxed and conducted in controlled environments.
Red Teaming
- Simulates real-world attack scenarios across multiple systems and vectors.
- Emphasizes testing an organization’s detection and response capabilities.
- Requires longer engagement periods for holistic assessments.
What Is PCI DSS?
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a global framework designed to secure payment card data and protect transactions from fraud and theft. Governed by the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC), it sets requirements for safeguarding cardholder data across storage, processing, and transmission.
The latest version, PCI DSS 4.0.1 (previous PCI 3.0), enhances these measures to address modern cyber threats, introducing greater flexibility, continuous improvement, and customized security controls. This ensures businesses can proactively manage risks and maintain trust in a complex digital environment.
» Here's how to build a robust PCI DSS security strategy
Best Practices for PCI DSS Compliance
1. Regular Security Awareness Training
Ongoing training is essential to ensure that employees remain educated about evolving security threats, risks, and the best techniques for mitigating them.
Here's how:
- Conduct regular training sessions on topics like phishing, social engineering, password hygiene, and data handling.
- Use interactive training modules, simulations, and quizzes to enhance learning.
- Conduct periodic security awareness assessments to measure employee knowledge and understanding.
» Start with understanding the benefits of PCI DSS compliance
2. Strong Access Controls
Ensuring you restrict access permissions to certain employees limits potential access to sensitive data and systems to authorized personnel.
Here's how:
- Implement strong password policies, including complexity requirements and regular password changes.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for critical systems and privileged accounts.
- Implement role-based access controls (RBAC) to grant access to only necessary resources.
- Regularly review and audit access privileges to identify and revoke unnecessary permissions.
3. Secure Network Configuration
Secure configuration protects the network infrastructure from unauthorized access and attacks.
Here's how:
- Use firewalls to segment networks and control traffic flow.
- Implement strong network security policies, including secure configurations for routers, switches, and other network devices.
- Regularly monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and potential threats.
- InsertAssistantlinksHistory Encrypt sensitive data transmitted over the network.
» Confused about encryption? Compare asymmetric and symmetric encryption
4. Vulnerability Scanning and Patching
Getting on top of identifying vulnerabilities means that you can address them before they are exploited by attackers.
Here's how:
- Conduct regular vulnerability scans to identify weaknesses in systems and applications.
- Implement a patch management process to promptly apply security patches and updates.
- Use automated tools to streamline the patching process.
- Prioritize patching for critical vulnerabilities and systems.
» Compare vulnerability scans to penetration tests
5. Incident Response Planning
This ensures a timely and effective response to security incidents.
Here's how:
- Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security breaches.
- Establish incident response teams and assign roles and responsibilities.
- Conduct regular incident response drills and simulations to test the plan's effectiveness.
- Have a clear communication plan to inform stakeholders about incidents and their impact.
Why Penetration Testing Is Essential in PCI DSS Compliance
Understanding PCI DSS penetration tests is key to recognizing its pivotal role in maintaining compliance under PCI DSS 4.0.1. Requirement 11.4 outlines specific PCI DSS penetration testing requirements for regular internal and external penetration testing to ensure systems, networks, and applications within the cardholder data environment (CDE) remain secure.
» Make sure you avoid these PCI DSS pitfalls
Requirement 11: Test Security of Systems and Networks Regularly
Requirement 11 emphasizes the importance of regularly testing the security of the CDE to identify and address vulnerabilities. This includes PCI compliance penetration testing, vulnerability and risk assessments, and remediation activities.
Key Details of Requirement 11.4
11.4.1: Defined Penetration Testing Methodology
Organizations must implement a documented methodology for penetration testing that includes:
- Use of industry-accepted testing approaches.
- Coverage of the entire CDE perimeter and critical systems.
- Testing from both internal and external perspectives.
- Validation of segmentation and scope-reduction controls.
- Application-layer and network-layer penetration tests targeting known vulnerabilities.
- Consideration of threats and vulnerabilities encountered in the past 12 months.
- Retention of testing and remediation results for at least 12 months.
11.4.2: Internal Penetration Testing
Internal penetration testing must be:
- Conducted at least annually or after significant infrastructure or application changes.
- Performed by a qualified internal resource or an independent third party.
- Conducted with organizational independence of the tester, ensuring impartial results.
11.4.3: External Penetration Testing
External penetration testing must meet similar requirements as internal tests, ensuring vulnerabilities are identified from outside the organization’s network. This includes:
- Testing at least annually and after significant changes.
- Use of qualified and independent testers, whether internal or external.
11.4.4: Addressing Vulnerabilities
Organizations must:
- Prioritize and address vulnerabilities based on assessed risks.
- Conduct follow-up penetration testing to verify remediation of identified issues.
11.4.5: Penetration Testing for Segmentation Controls
For organizations using segmentation to isolate the CDE:
- Testing must be performed annually and after any changes to segmentation methods.
- All PCI segmentation testing controls must be validated for effectiveness.
- Confirm that the segmentation controls/methods are operational and effective, and isolate the CDE from all out-of-scope systems.
- Confirm the effectiveness of any use of isolation to separate systems with differing security levels (see Requirement 2.2.3).
- It must be performed by a qualified internal resource or qualified external third party.
11.4.6: Additional Requirements for Service Providers
If segmentation is used to isolate the CDE from other networks, penetration tests are performed on segmentation controls as follows:
- At least once every six months and after any changes to segmentation controls/methods.
- Covering all segmentation controls/methods in use.
- According to the entity’s defined penetration testing methodology.
- Confirming that the segmentation controls/methods are operational and effective, and isolate the CDE from all out-of-scope systems.
- Confirming effectiveness of any use of isolation to separate systems with differing security levels (see Requirement 2.2.3).
- Performed by a qualified internal resource or qualified external third party.
- Organizational independence of the tester exists (not required to be a QSA or ASV).
11.4.7: Requirements for Multi-Tenant Providers
Multi-tenant service providers must support their customers by meeting external penetration testing requirements for segmentation controls, as outlined in 11.4.3 and 11.4.4.
In short, tests must be performed annually or after significant changes, using a defined PCI penetration testing scope that covers the entire CDE, validating segmentation controls, and addressing application and network vulnerabilities.
Organizations must remediate identified risks, retain testing results for at least 12 months, and ensure tester independence. Service providers face stricter requirements, including more frequent segmentation testing to maintain robust compliance.
How to Ensure PCI DSS Requirements Through Penetration Testing
- Identify vulnerabilities: PCI DSS penetration testing is a critical tool for identifying external and internal vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit to access cardholder data. This proactive approach allows entities to address weaknesses promptly, protecting networks and system components from potential breaches.
- Internal network security: Internal penetration tests play a dual role: uncovering misconfigurations and vulnerabilities exploitable by attackers with some degree of internal access, and identifying gaps in the change control process by detecting previously unknown systems. These tests also verify the effectiveness of security controls operating within the Cardholder Data Environment (CDE), ensuring robust internal network protection.
- Validate segmentation: For entities using segmentation controls to isolate the CDE from untrusted networks, segmentation penetration testing validates the effectiveness of these controls. With this approach, these tests ensure that untrusted networks remain securely separated from the CDE, preserving the integrity of cardholder data.
How to Scope for PCI DSS: 7 Steps
Scoping may look different depending on your organization, application, data sensitivity, security posture, and relevancy to PCI DSS. Scoping for PCI DSS compliance is a crucial step for businesses to ensure they are meeting the necessary requirements without unnecessary resource allocation. Larger organizations may have multiple, larger applications and/or legacy systems, which you would need additional efforts to segment for compliance.
To scope for PCI DSS compliance requirements, follow these steps:
- Determine your business objectives: Start by understanding why your business needs to be PCI DSS compliant. This could be because you accept credit card payments, and compliance is mandatory for your industry or to build trust with customers. Are you interested in meeting compliance requirements or going beyond compliance and focusing on your security posture in its entirety?
- Identify cardholder data (CHD): Clearly identify and document where CHD is collected, stored, transmitted, or processed within your organization. CHD includes primary account numbers (PANs), cardholder names, expiration dates, and other sensitive information.
- Define the scope: Limit the scope of PCI DSS compliance to the systems, people, and processes that handle CHD. The goal is to minimize the systems that fall within the scope.
- Assess third-party relationships: Identify any third-party service providers, such as payment processors or cloud providers, that interact with CHD. Ensure they are also compliant and that their services are included in your scope.
- Review payment channels: Evaluate all payment channels in your organization, including e-commerce websites, point-of-sale (POS) terminals, mobile apps, and any other methods used to accept payments.
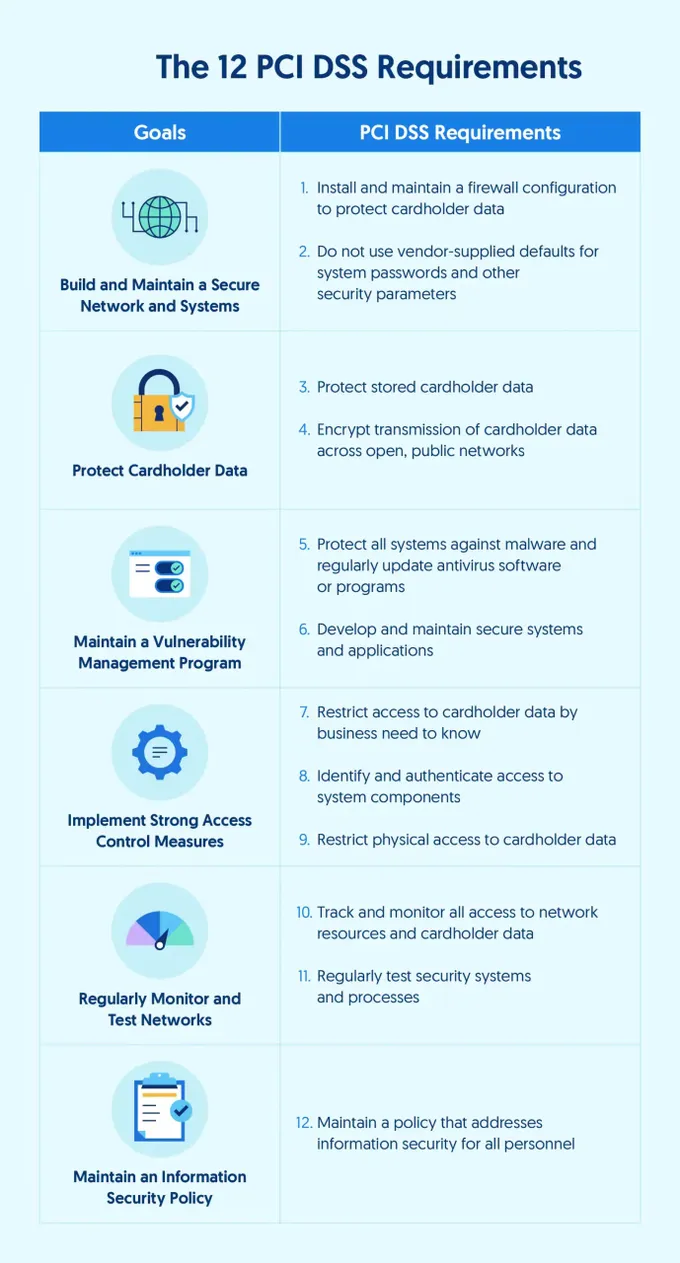
- Determine applicable requirements: Review the PCI DSS requirements (currently consisting of 12 requirements and numerous sub-requirements) and identify which ones are relevant to your scope. Not all requirements may apply if certain systems or processes are out of scope.
- Engage Qualified Security Assessors (QSAs): Engaging a Qualified Security Assessor (QSA) to validate compliance means finding a partner who understands where your business is coming from and what it's working towards. QSAs are independent entities authorized by the PCI Security Standards Council to assess PCI DSS compliance through their cyberservices.
Future Trends in PCI DSS
1. Cloud Security Takes Center Stage
As businesses move to cloud-based environments, PCI DSS compliance focuses on securing cardholder data in the cloud. This includes encrypting data, validating segmentation controls, and ensuring cloud providers meet PCI requirements. Regular vendor assessments and robust data protection strategies are critical to mitigating risks.
» Did you know? The cloud might not be safe anymore
2. API Security Under Scrutiny
APIs are central to modern payment systems but pose security challenges. PCI DSS highlights the importance of securing endpoints, enforcing strong access controls, and conducting regular vulnerability assessments. Monitoring API traffic and using secure development practices help prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
3. Increased Reliance on Automation
Automation is revolutionizing PCI DSS compliance by simplifying tasks like PCI scanning, log monitoring, and reporting. These tools enhance accuracy, reduce manual effort, and ensure businesses stay audit-ready while maintaining compliance with evolving standards.
Common Security Questions for PCI DSS Compliance
What type of pentest do I need for PCI DSS Compliance?
Penetration requirements for PCI DSS are quite specific compared to other security compliance frameworks. A QSA will need to see evidence of an application pentest, both internal and external infrastructure pentests as well as ensuring a segmentation test is conducted.
For those companies who have adopted PCI DSS version 4, biannual penetration testing is required, and segmentation testing in some cases.
Does OWASP top 10 training designed for developers satisfy PCI training requirements?
PCI DSS requires following secure coding guidelines and evidence that developers educate themselves on the latest best practices. OWASP top 10 training focuses on the latest vulnerabilities leading to the most damaging cybersecurity breaches, and how to avoid introducing them into code in the first place. The cyber security landscape is forever changing, and attackers are constantly honing their skills and inventing new attack strategies.
Therefore, per the PCI DSS 6.5 requirement, your developers must receive regular security training at least once a year. There are new versions of PCI DSS training based on new threats, and it is important to remain up to date with the latest training modules to help prevent security incidents. Software Secured offers OWASP top 10 training to help your developers keep up to date with the latest secure coding best practices.
How can you work with large vendors when you are just starting or are new to PCI DSS initiatives?
Every organization requires different security requirements. Each bank is different in terms of what they are looking for from vendors. Small and medium businesses can often struggle to answer vendor security questionnaires based on their understanding of risk, and security requirements that haven’t been put in place. SMB’s need compliance in order to close enterprise deals, among other tools and initiatives like training and penetration testing. For organizations with less experience with security, it is important to know what vendors are looking for when you are detailing your security posture.
Banks are looking for penetration testing reports and certificates to show all vulnerabilities and security gaps are closed within your SLAs. They also want to know more information around the vulnerabilities and what they are, and how each vulnerability was created (original root cause). Each organization varies, but those who are vetting vendors beyond compliance will ask more details about the risk to ensure they aren’t putting their company reputation or client data at risk.
Achieving PCI DSS Compliance and Strengthening Security With GRSee
Maintaining PCI DSS compliance goes beyond ticking boxes—it’s about creating a proactive and dynamic security posture to combat ever-evolving cyber threats. Penetration testing, whether internal, external, or segmentation-focused, is essential to identifying vulnerabilities, validating controls, and protecting sensitive cardholder data.
Partnering with experts like GRSee ensures your organization is equipped to meet PCI DSS requirements while staying resilient against future challenges. By adopting robust testing methodologies and a proactive approach, you can build a solid foundation for compliance, foster customer trust, and safeguard their digital ecosystems.
» Eager to reach PCI DSS compliance? Contact us to learn more about our enterprise and startup compliance services