Penetration Testing for SOC 2 Compliance: Essential Requirements (2025)
Uncover the must-know penetration testing essentials for SOC 2 compliance. Learn how to strengthen trust with robust controls and thorough risk management.
Published April 5, 2025.

SOC 2 (Service Organization Control 2) measures how well you protect, manage, and process customer data based on the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) principles.
Demonstrating strong SOC 2 compliance is a crucial step toward earning clients’ trust and standing out in today’s security-conscious market. Penetration testing plays a vital role in this process by showing how your controls perform against real-world threats rather than just on paper.
In this article, we explain the essential steps, emerging trends, and best practices for effectively incorporating penetration testing into your SOC 2 strategy.
» New to cybersecurity compliance? Gain expert SOC 2 auditing services for your business
Importance of SOC 2 Penetration Testing
Penetration testing for SOC 2 compliance focuses on simulating real-world cyberattacks to confirm whether your security measures genuinely defend against breaches. In other words, penetration testing boosts cybersecurity by bridging the gap between theoretical compliance and actual security.
You may already use audits to verify policies and controls on paper, but pentesting reveals how well those controls perform under active attack. By doing so, you bolster stakeholder trust, protect sensitive data, and meet the rigorous demands of SOC 2’s Trust Service Criteria (TSC).
Here's why penetration tests are vital for your business:
- Uncover hidden vulnerabilities: Pentests often reveal security gaps that essential audits miss.
- Validate security controls: Pentesting ensures each control works in practice, not just on paper.
- Protect stakeholder trust: Clients and regulators want proof you take data protection seriously.
- Stay ahead of evolving threats: Ongoing pentests let you adjust strategies as attack methods change.
» Learn more about the importance and benefits of pentesting
Emergence of Advanced Threat Simulation
Advanced threat simulation has become a vital evolution in penetration testing for SOC 2 compliance. Rather than relying on predictable or generic attack methods, you focus on sophisticated modeling that mirrors current hacker tactics. This approach includes adversary emulation, where testers replicate the actions of known threat actors.
Adversary emulation is a specialized form of testing where security teams adopt the same techniques, tactics, and procedures as real-world attackers. This method highlights which controls function well and where you must improve, ensuring you’re continually prepared for emerging threats.
By integrating these realistic simulations into your security assessments, you can pinpoint hidden vulnerabilities, strengthen your defenses against modern attacks, and maintain forward-thinking compliance.
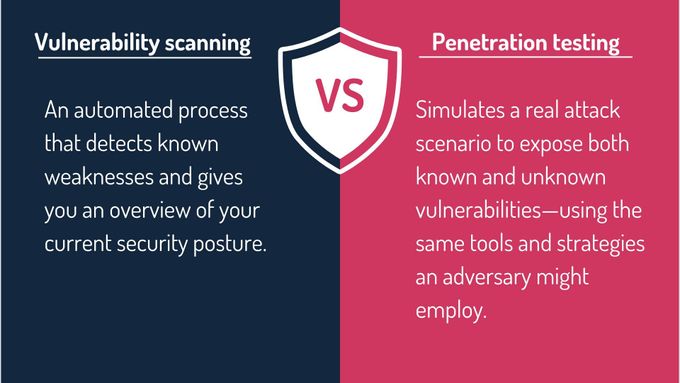
Vulnerability Scanning vs. Pentesting
Although scanning can be faster and more cost-effective, pentests provide deeper insights by actively trying to exploit possible weaknesses. It goes beyond checking boxes and offers a more realistic measure of whether you can protect sensitive data—one of the core objectives under SOC 2.
Here's a quick summary of the key differences between penetration testing and vulnerability scanning for SOC 2 compliance:
| Point of Comparison | Penetration Testing | Vulnerability Scanning |
|---|---|---|
| Time | More time-consuming due to manual testing and analysis | Faster due to automated scanning tools |
| Cost | Typically higher because of the specialized expertise required | Generally lower because automation reduces labor |
| Depth | Discovers both known and unknown vulnerabilities; demonstrates real impact | Focuses on identifying known vulnerabilities and doesn't exploit them |
» Find out more about how SOC 2 strengthens your security posture
Types of SOC 2 Penetration Testing
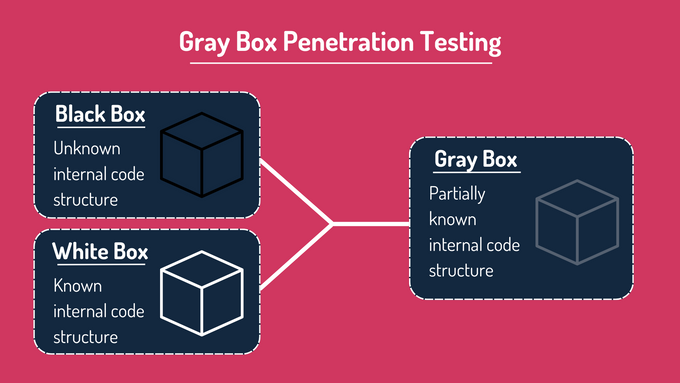
When it comes to SOC 2 compliance, you can choose among three main types of penetration testing:
- Black-box
- White-box
- Gray-box
Each approach varies in the level of system knowledge granted to testers and in how closely the test environment resembles an actual attack scenario.
While black-box testing offers an external view and white-box focuses on internal details, gray-box testing often strikes the ideal balance by combining partial knowledge of the system with realistic attack simulations.
Pros and Cons of Each Approach
1. Black-Box Testing
Pros
- Mimics a completely unknown attacker’s perspective
- Uncovers vulnerabilities visible from the outside
Cons
- May miss deep or internal weaknesses
- Can require more time and resources to explore every path
When to choose black box: You want to see how an attacker without prior knowledge could breach your public-facing services.
2. White-Box Testing
Pros
- Offers complete visibility into code, architecture, and configurations
- Typically covers more ground quickly
Cons
- Less representative of an external threat actor’s methods
- Testers might focus too heavily on known flaws
When to choose white box: You have complex systems needing thorough code reviews or are testing under tight time constraints.
3. Gray-Box Testing
Pros
- Balances external attacker realism with insider knowledge of the system.
- Efficiently finds both obvious and hidden issues.
Cons
- Requires careful scoping to ensure testers use partial system insights effectively.
Why gray-box pentesting is best for SOC 2: You simulate a real-world attacker who knows some aspects of your systems, uncovering subtle weaknesses without losing the external attacker’s viewpoint.
» Learn more: Our guide to gray-box penetration testing
Common Vulnerabilities Uncovered in SOC 2 Pentests
Penetration tests designed for SOC 2 often reveal several recurring security issues that can jeopardize customer data. By identifying and preventing cybersecurity disasters, you can prioritize fixes that bolster your compliance efforts and protect key business functions.
1. Weak Authentication and Authorization
Attackers can easily gain unauthorized access to sensitive data if systems lack strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and proper access controls.
How to fix or prevent this:
- Enforce robust password policies and multifactor authentication (MFA)
- Conduct periodic access audits, ensuring every user has the least privilege needed to perform their tasks
2. Unpatched Software and Known Vulnerabilities
Outdated software with known security flaws can be exploited by attackers to compromise systems and steal data.
How to fix or prevent this:
- Implement a structured patch management program
- Use automated tools to detect outdated software and apply updates promptly before attackers exploit them
3. Misconfigured Cloud Services
Improperly configured cloud storage, databases, and other services can expose sensitive data to unauthorized access.
How to fix or prevent this:
- Review cloud configurations regularly, limiting user privileges and encrypting sensitive data
- Platforms like AWS Config or Azure Security Center can help identify gaps quickly
» Protect your business's sensitive data through AWS penetration testing
4. Insecure APIs
Weaknesses in application programming interfaces (APIs) can allow attackers to bypass security controls and access sensitive data or functionality.
How to fix or prevent this:
- Conduct in-depth code reviews, implement secure coding practices, and deploy Web Application Firewalls (WAFs).
- Run API security tests before each release cycle to catch potential flaws early.
Requirements & Best Practices for SOC 2 Penetration Testing
While SOC 2 doesn’t explicitly mandate penetration testing, the framework strongly encourages it through its Trust Service Criteria (TSC). Most auditors also advocate regular pentests as a proactive measure.
In doing so, you satisfy auditors and reassure customers that you take data protection seriously. Successfully integrating penetration testing into your SOC 2 efforts requires a well-defined, repeatable, and secure development lifecycle.
Here are the basic steps to follow for pentesting:
- Scope: Identify critical assets, data flows, and systems that require testing.
- Testing: Security specialists (internal or external) simulate real-life attacks, then map each vulnerability to its relevant TSC.
- Remediation: Prioritize fixes by severity, focusing on the most critical issues first.
- Retesting: Confirm that no new weaknesses have emerged and that existing gaps are fully resolved.
» Do this before you outsource: Learn the key factors for hiring a risk assessment provider
Scope Your Penetration Tests
Defining the boundaries of your SOC 2 penetration test is essential for accurate results. You should include all critical assets that store, process, or transmit sensitive data—from user-facing SaaS or web platforms to administrative portals, APIs, and internal infrastructure.
This strategy ensures you address both external threats and potential internal weaknesses. Conducting tests in a staging environment is also advisable so you can spot and remediate vulnerabilities without risking live operations.
Prioritize Key Areas During SOC 2 Penetration Tests
When scheduling your tests, you should pay special attention to systems that handle the highest volume of sensitive data or regularly interface with the internet. By targeting these critical points first, you minimize the risk of a serious breach and ensure continuity for essential business processes.
High-sensitivity systems to consider include:
- Network infrastructure: Firewalls, routers, and load balancers that regulate data traffic.
- Web applications: Publicly accessible websites and SaaS platforms where users submit critical information.
- APIs: Bridges between different services and databases, often carrying sensitive transaction data.
- Internal systems: Administrative tools and corporate networks that insiders or lateral attacks can exploit.
Frequency and Triggers for Testing
You should perform SOC 2 penetration tests at least once a year to stay ahead of evolving threats. However, you must also retest whenever significant changes occur in your environment. These triggers may include large-scale cloud migrations, software deployments, and security incidents.
Industry Variations and Challenges
SOC 2 penetration testing requirements can shift depending on your sector. Here are some top concerns by industry:
- Education: FERPA compliance and distributed network infrastructures.
- Technology: Cloud security risks, API vulnerabilities, and ongoing software updates.
- Finance: Identity theft and large-scale fraud risks.
- Healthcare: HIPAA compliance and patient privacy violations.
» Learn more about cybersecurity risks in healthcare
Documentation and Reporting
Your penetration testing report should be both comprehensive and accessible. Achieve this by following these steps:
- Begin with an executive summary highlighting major findings and risk levels in plain language
- Follow with a methodology and scope overview, explaining exactly how you conducted the test
- Present vulnerabilities in order of severity, accompanied by actionable remediation steps and evidence like screenshots or logs
- Finally, map each finding to the relevant SOC 2 Trust Service Criteria to demonstrate precise alignment with compliance requirements
Balancing Cost and Complexity While Meeting SOC 2 Requirements
SOC 2 penetration testing can become resource-intensive, but you have practical strategies to keep costs manageable without sacrificing security. By prioritizing high-impact areas first and adopting a gradual test plan, you can align with auditor expectations, maintain ongoing compliance, and keep your data safe.
- Phased testing: Focus first on the systems handling the most sensitive data, then expand to lower-risk areas. This approach spreads out the investment, making it easier to incorporate improvements over time.
- Timely remediation: Address vulnerabilities as soon as you find them, prioritizing by severity. Prompt fixes minimize risk exposure and help you maintain continuous SOC 2 readiness.
- Leverage automated tools: Use scanning and detection tools for initial vulnerability sweeps. Automation speeds up the discovery of common weaknesses and frees your team to handle complex, manual testing scenarios.
- Adopt a risk-based approach: Assess which assets carry the greatest potential impact if compromised and focus resources accordingly. This ensures you tackle the highest risks first.
Mapping Penetration Test Results to SOC 2 Trust Service Criteria
Penetration testing drives real-world insights into how your security controls perform under attack. By aligning these findings with the five SOC 2 Trust Service Criteria (outlined below), you gain a clear view of where you meet compliance requirements and where you need to strengthen defenses.
Here are the five SOC 2 Trust Service Criteria (TSC):
- Security: Testing reveals how effectively your safeguards block unauthorized access.
- Availability: You maintain uptime and service reliability by identifying disruptions before they occur.
- Confidentiality: Pentest results show if sensitive data could be exposed and guide remediation steps.
- Processing integrity: Risk assessments ensure data processing workflows aren’t prone to tampering or errors.
- Privacy: A thorough test uncovers gaps in personal data protection, supporting regulatory compliance.
Here's how SOC 2 pentest outcomes align with each TSC:
| TSC Domain | Pentesting Objectives |
|---|---|
| Security | Identify exploitable weaknesses that compromise security controls. |
| Availability | Ensure systems remain accessible even under malicious attempts. |
| Confidentiality | Protect sensitive information from unauthorized exposure. |
| Processing integrity | Validate accuracy and completeness of data throughout transactions. |
| Privacy | Verify compliance with data privacy rules and highlight potential leaks. |
GRSee: Your Partner in Applications and Cloud Security
At GRSee, we specialize in end-to-end cybersecurity services—spanning cloud environments, applications, and infrastructure—to ensure your SOC 2 certification process runs smoothly. Our team engages directly with you and your auditor to conduct a gap analysis, outline a tailored work plan, and perform robust penetration testing. We also compile the necessary documentation and lead the entire audit to certification.
Through this hands-on approach, we reduce the time, resources, and costs that often accompany SOC 2 assessments. Whether you need cloud security testing, application reviews, or holistic cybersecurity planning, GRSee offers proven expertise to strengthen your defenses, streamline compliance, and support your organization’s long-term resilience.
» Ready to get started? Let's get in touch