What Is the NIST Cybersecurity Standard?
Explore how the NIST cybersecurity standards offer a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks, protecting sensitive information, and ensuring a robust security posture.
Published May 18, 2025.

Adopting the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) isn't just about ticking compliance boxes—it's about giving your organization a real, structured way to tackle cyber risk. Whether you're just starting out or looking to improve existing efforts, the NIST cybersecurity framework offers a flexible structure that can be tailored to your risk level, goals, and industry.
In this blog, we’ll explore how it works, the support frameworks that complement it, and how you can use it to make practical, long-term improvements in your cybersecurity posture.
» Contact us to see how our startup and enterprise security services can help
What Is the NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
The NIST CSF is a set of policies and guidelines designed to help organizations manage and reduce cybersecurity risks. Developed in collaboration with government agencies, industry leaders, and academic experts, the framework responds to the increasing threat of cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure.
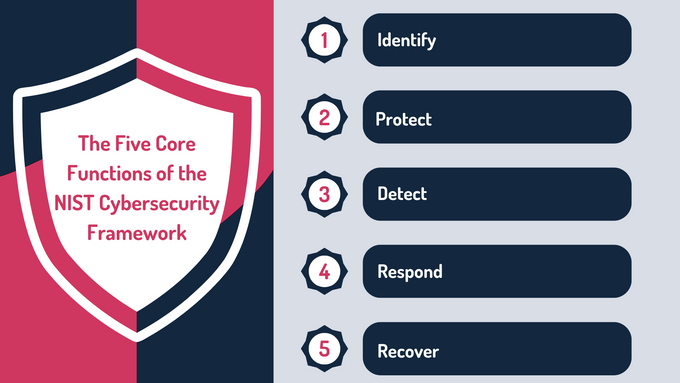
Take Note: The NIST CSF uses categories and subcategories to break large goals into manageable steps, helping organizations achieve effective security. These categories are organized under five main functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover.
Benefits of Adopting the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
- Improved operational resilience: By following the NIST CSF’s structured approach, organizations can identify vulnerabilities, prevent incidents, and carry out swift responses when threats occur. This helps reduce downtime and maintain service delivery even during cyberattacks.
- Enhanced risk visibility: The framework promotes regular risk assessments and resource inventories, making it easier to identify vulnerabilities and understand how critical systems are exposed. In one case, after implementing the NIST security framework, a clinic identified and replaced outdated systems, significantly reducing its vulnerability.
- Increased stakeholder confidence: Adopting a recognized framework like the NIST CSF builds trust among customers, partners, and investors. It demonstrates a clear commitment to security and data protection. Vendors aligning with NIST have been able to gain faster onboarding approvals with larger enterprises due to their verifiable compliance posture.
» Learn more: NIST vs. ISO 27001
The 5 Core Functions of the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
1. Identify
This helps organizations understand and manage cybersecurity risks of the systems, the people, assets, data, and capabilities. This step is essential because it builds the foundation for all other functions.
Activities include
- Asset inventory: Keeping a detailed, updated list of all hardware, software, and data assets across the organization.
- Risk assessments: Identifying and evaluating the potential impact of threats and vulnerabilities on business operations.
- Business environment analysis: Understanding the organization’s mission, goals, and critical functions to prioritize cybersecurity efforts.
- Governance policies: Defining roles, responsibilities, and accountability for cybersecurity decisions and risk management.
2. Protect
This ensures that safeguards are in place to limit or contain the impact of a potential cyber event. This function helps teams proactively block attacks before they happen by enforcing security policies and awareness programs.
Activities include
- Access controls: Restricting access to systems and data based on roles and need-to-know principles.
- Multi-factor authentication: Adding extra layers of security to verify user identities before granting access.
- Encryption: Protecting data at rest and in transit by converting it into unreadable formats for unauthorized users.
- Data loss prevention (DLP): Using tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization unintentionally.
- User training and awareness: Educating employees about phishing, social engineering, and safe digital behavior.
3. Detect
This identifies cybersecurity threats quickly and more accurately. Early detection is vital, as it can be the difference between a minor incident and a major breach.
Activities include
Continuous monitoring: Keeping an eye on systems and networks 24/7 for unusual activity or policy violations.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Collecting and analyzing logs and alerts from multiple sources to identify potential threats.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Detecting unauthorized access or malicious activity on the network.
- Anomaly detection: Using behavioral baselines to flag deviations that could signal a compromise or internal misuse.
4. Respond
This ensures that organizations take swift action after a cybersecurity event. It eliminates confusion, reduces panic, and ensures every team member knows their role. A well-tested response plan limits downtime and financial loss.
Activities include
- Incident response plans: Documented procedures that guide the organization’s actions during and after a cybersecurity event.
- Clear communication protocols: Predefined internal and external messaging guidelines during an incident, including stakeholder updates.
- Forensic analysis: Investigating how the breach occurred, what was affected, and what evidence needs to be preserved.
- Mitigation strategies: This involves isolating affected systems, blocking malicious traffic, and addressing vulnerabilities quickly to contain the threat and prevent further damage.
5. Recover
This focuses on restoring capabilities or services after a cybersecurity incident. A strong recovery plan can restore trust, resume operations quickly, and prevent long-term damage.
Activities include
Backup management: Ensuring critical data is regularly backed up, stored securely, and can be quickly restored when needed.
- Disaster recovery plans: Comprehensive strategies that detail how to resume IT services and business functions after major disruptions.
- Post-incident reviews: Assessing what happened, what worked, and what didn’t to improve the organization’s future response and resilience.
- Communication with stakeholders: Informing clients, partners, and regulators about the incident and recovery progress to maintain transparency and trust.
Take Note: Organizations can adjust the NIST CSF based on what matters most to them like regulations, business goals, or the kinds of threats they face. A hospital may focus on patient data protection, while a bank may prioritize fraud detection.
» Here are 6 things you should know before hiring a risk assessment service provider
The NIST CSF Implementation Tiers
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework’s Implementation Tiers consist of four levels that help organizations assess how well their cybersecurity practices align with their goals, risk levels, and the threats they face.
- Partial: Companies at this level lack a clear cybersecurity strategy and often fail to prioritize security risks. They need to develop processes to handle cybersecurity concerns effectively.
- Risk-informed: Organizations have a basic awareness of threats and some policies in place. However, they often lack a cohesive strategy and struggle with inconsistent implementation across various departments.
- Repeatable: This tier is for organizations with established risk management and cybersecurity practices that are approved by leadership. These companies are better prepared to address vulnerabilities, risks, and threats effectively.
- Adaptive: In this tier, organizations employ advanced, adaptive cybersecurity practices that continuously evolve to address emerging threats. These companies use technologies such as machine learning, AI-driven systems, and SIEM to detect and respond to incidents more effectively.
» Here are the disasters you can avoid by tackling cybersecurity on time
Challenges and Solutions in Adopting NIST CSF
Complexity and Overwhelm
- Challenge: The NIST CSF's many parts, functions, categories, and tiers can be confusing, particularly for small teams lacking deep security knowledge.
- Strategy: Start small, focus on the most important risks, and link key assets to NIST functions. Use accessible resources to guide you through the process, simplifying the journey toward effective cybersecurity management.
Lack of Internal Alignment
- Challenge: Different departments, such as IT, compliance, and leadership, may have varying security goals, making consistent framework application difficult.
- Strategy: Bring all departments together in a planning session. Appoint a project leader to align the framework with the business goals.
Resource Constraints
- Challenge: Mid-sized and smaller organizations often struggle to dedicate sufficient budget, time, or staff to fully implement the NIST CSF.
- Strategy: Prioritize implementation by focusing on high-risk areas. Use the Tier system to align actions with your organization’s current capabilities. This helps prioritize steps based on where your cybersecurity maturity currently stands. You can also seek external support from consultants like GRSee when internal resources are limited.
» Do you have a startup? Here are some cyber tips to improve your security
Additional NIST Cybersecurity Frameworks for Specialized Compliance Needs
NIST SP 800-53: Security and Privacy Controls
- This framework outlines comprehensive security and privacy controls for federal systems and organizations, offering detailed technical measures to achieve compliance with the Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA).
- It complements the NIST CSF by specifying the implementation details needed for high-security environments, particularly in government-regulated sectors.
NIST SP 800-171: Protecting Controlled Unclassified Information
- This framework focuses on protecting Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) for federal contractors.
- It simplifies SP 800-53’s controls, making them applicable to nonfederal systems, and aligns with the NIST CSF by focusing on confidentiality requirements for industries handling sensitive government data, such as defense and supply chains.
» Want to boost your organization's security? Implement the CIA triad
How GRSee Can Help You Apply the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
At GRSee Consulting, we guide you through adopting the NIST Cybersecurity Framework in a way that fits your business—not a one-size-fits-all method. We start by helping you understand your current maturity through a gap analysis based on the framework’s five core functions.
From there, we build a step-by-step plan aligned with your specific industry needs and regulatory pressures like HIPAA or PCI DSS. Our clear reporting helps you prioritize actions and get leadership on board. We’re here to make the NIST cybersecurity standard practical and achievable for you.
» Ready to take control of your cybersecurity? Contact us to get started