How to Fortify Your Business Against Password Spraying Attacks
Discover essential strategies to protect your organization from cybersecurity threats. Learn how implementing robust security measures can help safeguard your accounts and maintain your business's integrity.
Published April 5, 2025.

Over the last decade, the digital world has changed in various ways, with an increasing threat from password spraying attacks that jeopardize business security. Unlike brute-force attacks, password spraying targets multiple accounts with common passwords without raising red flags. This allows attackers to access numerous accounts with minimal effort, exploiting weak or reused employee passwords.
The consequences (such as data breaches and reputational harm) are significant—especially in high-stakes sectors like finance, healthcare, and government. Here's what you can do to protect your business from password spraying attacks.
» Let the experts handle your password needs with our startup and enterprise services
Understanding Password Spraying
Password spraying is a type of cyberattack in which hackers attempt to gain unauthorized access to multiple accounts by testing commonly used passwords, such as "password123" or "welcome." They rely on the probability that some of the organization's users will resort to weak passwords that are easy to remember.
This tactic allows attackers to avoid detection mechanisms that would flag repeated attempts on a single account, making it especially dangerous for organizations with weak password management policies.
In simple terms, the method exploits weak, default, or reused passwords that employees might use across multiple platforms. Then, distributing their efforts across multiple accounts allows hackers to evade detection by security systems.
» Check out these cyber tips for your startup plan
Why Larger Businesses Are More Vulnerable to Password Spraying
- High user account volume: Large organizations often have numerous user accounts, increasing the likelihood of weak or reused passwords within the system.
- Simple or predictable passwords: Despite existing password policies, some employees (especially those less tech-savvy individuals) inevitably set simple or common passwords.
- Legacy systems & decentralized security: Many large organizations rely on outdated systems or inconsistent security practices, creating gaps in their defenses.
- Attackers exploit inconsistencies: Cybercriminals use common passwords across multiple accounts to avoid detection and gain unauthorized access.
Vulnerable organizations include government agencies, educational institutions, healthcare providers, and multinational corporations.
These organizations typically have numerous users and extensive IT infrastructures, making it easier for attackers to exploit weak password practices.
» Looking to beef up your cyber security? Learn about the CIA triad
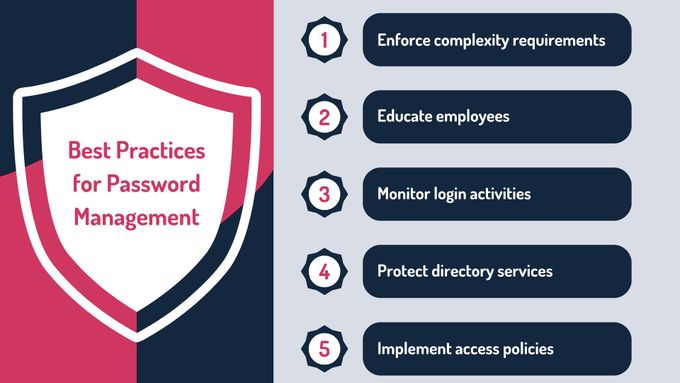
5 Best Practices for Password Management
1. Enforce Complexity Requirements and Minimum Length
Organizations should enforce complexity requirements, ensuring that passwords contain a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Additional tips for setting passwords:
- Minimum length requirement: Set a minimum password length of at least 12 characters to make passwords harder to guess or crack.
- Prohibit common passwords: Implement filters to block widely used or compromised passwords, further enhancing security.
2. Educate Employees
Regular security awareness programs can inform staff about the risks of poor password hygiene (the practice of choosing and maintaining passwords), as well as the tactics used in these types of attacks.
Employees should also receive training to recognize phishing attempts, which are often employed to steal login credentials. Simulated phishing exercises provide practical experience and help reinforce good security practices, enabling employees to identify and report potential threats more effectively.
3. Monitor Login Activities
Monitoring login activities is important for detecting early signs of suspicious behavior. Consider the following tools:
- Security Information and Event Management Systems (SIEMs) analyze authentication logs for anomalies like repeated failed login attempts
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) tools identify unusual login patterns, such as access from unfamiliar locations or simultaneous logins
When combined with alerting mechanisms, these tools provide immediate notifications to administrators for quick responses to potential threats.
4. Protect Directory Services
Organizations should focus on hardening active directories by addressing common misconfigurations and enforcing least privilege access policies.
Monitoring for unusual queries can also help identify attackers attempting to enumerate valid usernames. Disabling anonymous access (null sessions) further prevents the exploitation of directory services.
5. Implement Conditional Access Policies
Implementing conditional access policies helps limit unauthorized access by enforcing stricter measures for logins from unrecognized devices or locations, which is crucial in protecting against ransomware attacks.
Risk-based authentication allows organizations to enforce stricter measures for users logging in from unrecognized devices or locations. Additionally, geo-restriction policies can further mitigate risks, limiting or scrutinizing access attempts from foreign countries where the organization doesn’t operate, thereby reducing the chances of potential attacks.
» Here’s our comprehensive guide on effectively dealing with ransomware
The Role of MFA in Securing Systems
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) strengthens system security by requiring additional verification beyond just the password, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
In password spraying attacks, hackers exploit weak or common passwords. With MFA, even if a password is guessed, attackers must provide a second form of verification such as a code or biometric data. This added layer makes it nearly impossible for attackers to compromise systems based solely on stolen passwords.
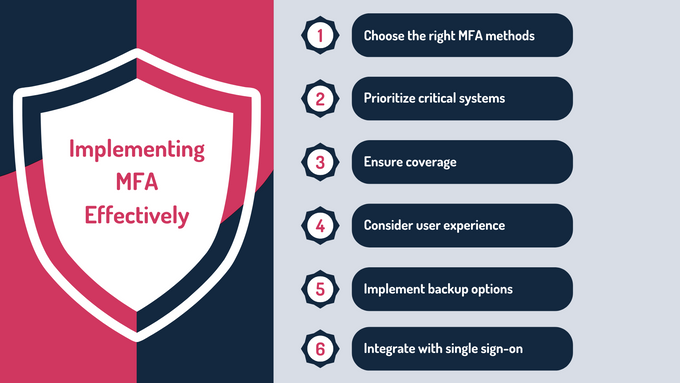
1. Choose the Right MFA Methods
Use authenticator apps like Google Authenticator or hardware tokens such as YubiKey to provide robust security and avoid the vulnerabilities associated with SMS codes. For added security, incorporate biometric options like fingerprint or facial recognition where possible.
2. Prioritize Critical Systems
Implement MFA on high-risk systems that handle sensitive data or provide privileged access, such as administrative and financial platforms. Protect remote access points, including VPNs and cloud services, which are common targets for attackers.
» Find out why the cloud might not be safe anymore
3. Ensure Comprehensive Coverage
Apply MFA to all accounts within the organization, including employees, contractors, and third-party integrations, to avoid leaving any weak links. Extend MFA to external partners and services to close potential security gaps.
4. Consider User Experience
Select MFA methods that balance security with ease of use to encourage widespread adoption. Educate employees on the importance of MFA and provide training on how to use it effectively.
5. Implement Backup Options
Offer alternative verification methods like backup codes in case users lose access to their primary MFA device and develop secure account recovery protocols to allow users to regain access without compromising security.
6. Integrate With Single Sign-On (SSO)
Streamline the login process by integrating MFA with SSO, simplifying access to multiple applications while maintaining high security. Additionally, centralized management of authentication policies using SSO simplifies enforcement and monitoring.
» Understand the benefits of a secure development lifecycle
Tools for Preventing Password Spraying
Utilizing tools can reduce the risk of password spraying attacks. Let's examine the various tools available to strengthen security systems and how they can be tailored to meet an organization's needs and architecture.
Disclaimer: These are just examples of available tools. It's important to consider different technologies that best suit your organization's specific needs and network architecture.
5 Types of Password Spraying Prevention Tools
1. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
- Splunk: Provides real-time monitoring and analysis of security events, helping detect threats quickly and efficiently.
- IBM QRadar: Offers comprehensive visibility and intelligent insights into security threats, supporting early detection and incident response.
2. User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
- Exabeam: Uses machine learning to detect anomalous user behavior, uncovering potential insider threats and risky actions.
- LogRhythm UEBA: Analyzes user activities, identifies patterns indicative of security risks, and flags suspicious behavior.
3. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
- Duo security: Ensures secure access through multi-factor authentication, adding extra layers of verification and device visibility.
- Microsoft authenticator: Provides easy and secure sign-ins with additional verification steps, enhancing user security.
4. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Okta: Centralizes identity management across applications and enforces strong authentication, ensuring secure user access.
- Ping Identity: Enables seamless access to applications with advanced identity solutions, enhancing both security and usability.
5. Advanced Authentication Protocols
- FIDO2: Supports passwordless authentication methods for enhanced security, eliminating the reliance on traditional passwords.
- WebAuthn: Facilitates strong authentication using public key cryptography and biometrics, offering a secure alternative to passwords.
» Don’t leave it too late: Explore the disasters you can avoid by proactively addressing your cybersecurity needs
Striking the Right Balance: Security vs Convenience
Striking the right balance between security and convenience can be challenging for businesses aiming to protect against password spraying attacks.
While implementing robust security measures is essential, these improvements often sacrifice user convenience. Stronger protection mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strict password policies, may slightly hinder user efficiency, but they significantly enhance the organization's security posture.
Unfortunately, security can't be improved without some reduction in convenience. But with thoughtful implementation, security strategies can be designed to minimize disruption while effectively protecting against threats.
» Want to ensure your security? Here are the standards you should meet
Immediate Steps to Take After Detecting a Password Spraying Attack
When a password spraying attack is detected, swift and decisive action is crucial to contain the threat and mitigate potential damage. Here are six immediate steps businesses should take to safeguard their systems and prevent further compromise:
- Identify and lock affected accounts: Immediately identify accounts that show signs of unauthorized access or multiple failed login attempts and temporarily lock or suspend them to prevent further access.
- Enforce password resets: Prompt affected users to reset their passwords, ensuring that the new ones meet strong complexity and length requirements.
- Implement MFA: Enable MFA across all user accounts to ensure that even if passwords are compromised, an additional layer of verification is required for access.
- Block suspicious IP addresses: Use firewall or intrusion prevention systems to block the IP addresses associated with the attack.
- Enhance monitoring and logging: Increase real-time monitoring of authentication logs and network traffic to detect any additional suspicious activity and improve visibility into potential threats.
- Review and strengthen security policies: Conduct an immediate review of your security policies—including password management, account lockout settings, and user access control—to prevent future attacks.
» Want to learn more about protecting your systems from threats? Read how malware can bypass endpoint protection
How GRSee Offers Solutions Against Password Spraying
At GRSee, we provide a comprehensive suite of cyberservices to help businesses strengthen their defenses against password spraying attacks. With our detailed gap analysis, we assess the existing security landscape, identifying weaknesses and recommending tailored strategies to enhance password policies and overall security practices. Moreover, our penetration testing service simulates real-world cyberattacks to uncover vulnerabilities, enabling businesses to proactively mitigate risks.
We also focus on the human element of security with employee training programs that educate staff on recognizing and avoiding cybersecurity threats.
» Contact us to strengthen your security against password spraying attacks with effective strategies and tools